WebXR
[ comments ]
The WebXR Device API provides access to input (pose information from headset and controllers) and output (hardware display) capabilities commonly associated with Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) devices. It allows you develop and host VR and AR experiences on the web.
You can read more about the goals of this standardisation effort by reading the WebXR Explainer.
What does this mean...

For phones:
Enable VR by providing pose information and allowing the WebGL scene to be rendered side by side to be placed in a headset like the Cardboard
Enable AR by using the platforms AR capabilities such as ARCore to render the WebGL scene onto the users environment like a magic window.
For Desktops:
Desktop computers can make use of tethered VR hardware such as the Oculus Rift or HTC Vive to display the VR scene
For standalone AR Headsets:
Enable AR by using the platforms AR capabilities to render the WebGL scene immersively onto the users environment.
For standalone VR Headsets:
Enable VR by rendering the scene using the platforms VR capabilities.
Try out some Demos
allow="xr-spatial-tracking" is required.These are samples from the WebXR Samples from the Immersive Web Working Group They use a very minimal libary to show how one can make use of the WebXR Device API directly.
Benefits of doing XR on the Web
- Instant deployment to every XR platform with a WebXR enabled Web Browser
- Future proof experiences, new AR and VR hardware comes about regularly, your experience should continue working on new hardware without needing to push new code.
- An experience can choose to target both VR and AR, Handheld and head mounted devices with a single release. Minimal code changes needed to support VR and AR together.
- No app stores or large downloads required, users get immediate access to your experience without needing to leave your web site.
- Since the rendering is handled by WebGL, which has been around since 2011, you gain the benefit of WebGL's rich development tool ecosystem and a large, active developer community.
WebXR in the Real World
Hello WebXR
Mozilla Mixed Reality
The demo is designed as a playground where you can try different experiences and interactions in VR, and introduce newcomers to the VR world and its special language in a smooth, easy and nice way.
XR Dinosaurs
Brandon Jones
Welcome to the web's virtual Dinosaur Park!
We've used the magic of your browser to bring back a friendly pack of prehistoric pals.
Our dinosaurs can be viewed with a variety of Virtual Reality headsets, Augmented Reality headsets and phones, or directly in your browser.
What You Don't Know
Jono & Mr. Doob
Dive into the creative process of avant-pop artist Matthew Dear from his new single of the same name. Floating above you is a magic eight-ball reciting lyrics. In the distance planetary objects orbit around you to the beat. And directly ahead is an elastic donut which bounces, bulges, and twists to the complex melodies.
Getting started building a WebXR Website
These are brief guides to building a site which uses and AR and VR.
The WebXR device API relies on graphics APIs like WebGL & WebGL2 to work, these graphics libraries and frameworks come with WebXR support built in.
A-Frame is a web framework for building 3D/AR/VR experiences using a combination of HTML and Javascript.
A-Frame is based on three.js and has a large community, as well as lots of community-made custom elements and components.
position="-1 0.5 -3" rotation="0 45 0" color="#4CC3D9">
position="0 1.25 -5" radius="1.25" color="#EF2D5E">
position="1 0.75 -3" radius="0.5" height="1.5" color="#FFC65D">
position="0 0 -4" rotation="-90 0 0" width="4" height="4" color="#7BC8A4">
color="#ECECEC">
Babylon.js is an easy to use real-time 3D game engine built using TypeScript. It has full WebXR support out of the box, including gaze and teleportation support, AR experimental features and more. To simplify WebXR development Babylon.js offers the WebXR Experience Helper, which is the one-stop-shop for all XR-related functionalities.
To get started use the Babylon.js playground, or try these demos:
To start on your own use this simple template:
http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html" charset="utf-8" />
For advanced examples and documentation see the Babylon.js WebXR documentation page
Model viewer is a custom HTML element for displaying 3D models and vieweing them in AR
AR
src="examples/assets/Astronaut.glb" ar alt="A 3D model of an astronaut" auto-rotate camera-controls background-color="#455A64">
p5.xr is an add-on for p5.js, a Javascript library that makes coding accessible for artists, designers, educators, and beginners. p5.xr adds the ability to run p5 sketches in Augmented Reality or Virtual Reality.
p5.xr also works in the p5.js online editor, simply add a script tag pointing to the latest p5.xr release in the index.html file.
function preload() {
createVRCanvas();
}
function setup() {
setVRBackgroundColor(0, 0, 255);
angleMode(DEGREES);
}
function draw() {
rotateX(-90);
fill(0, 255, 0);
noStroke();
plane(10, 10);
}
PlayCanvas is an open-source game engine. It uses HTML5 and WebGL to run games and other interactive 3D content in any mobile or desktop browser.
Full documentation available on the PlayCanvas Developer site including API reference. Also check out XR tutorials with sources using online Editor as well as engine-only examples and their source code.
Below is basic example of setting up PlayCanvas application, simple scene with light and some cubes aranged in grid. And Immersive VR session on click/touch if WebXR is supported:
lang="en">
react-xr is a collection of hooks to help you build XR experiences in react-three-fiber applications. To make a VR React application we’ll use the following stack:

Three.js is a library for 3D graphics, react-three-fiber is react renderer for Three.js, drei is a collection of reusable components for r3f and react-xr is a collection of hooks to help you build XR experiences in react-three-fiber applications.
react-xr
As soon as you have a 3D scene using react-three-fiber you can make it available in VR or AR with react-xr.
For that, the only thing you need to do is to replace component with
Take a look at those simple example here:
VR
https://codesandbox.io/s/react-xr-simple-demo-8i9ro
AR
https://codesandbox.io/s/react-xr-simple-ar-demo-8w8hm
You’ll notice that you now have “Enter VR/AR” button available at the bottom of the screen that should start the experience.
Adding controllers
To add controllers you can use a component from react-xr package called
<VRCanvas>/* or ARCanvas */
<DefaultXRControllers />
VRCanvas>
Interactivity
To interact with objects using controllers you can use
here is a short example
const [isHovered, setIsHovered] = useState(false)
return (
<Interactive onSelect={() => console.log('clicked!')} onHover={() => setIsHovered(true)} onBlur={() => setIsHovered(false)}>
<Box />
Interactive>
)
You can also see this method in the two VR and AR examples aboves
Learn more
We barely scratched the surface of what is possible with libraries like react-three-fiber and react-xr, I encourage you to check out more examples in GitHub repositories here and here. Remember, every r3f scene can be easily adjusted to be available in WebXR.
Three.js is a cross-browser JavaScript library used to create and display animated 3D computer graphics in a web browser. It has a large community, good docs, and many examples.
Using VR is largely the same as regular Three.js applications. Setup the scene, camera, and renderer. The major difference
is setting the vr.enabled flag to true on the renderer. There is an optional VRButton class to make a button that
will enter and exit VR for you.
For more info, see this guide to VR in Three.js and the WebXR examples.
Here is a full example that sets up a scene with a rotating red cube.
lang="en">
charset="UTF-8">
Here is a full example of an immersive-ar demo made using three.js
lang="en">
Unity is a GUI based game engine. It has a number of unofficial WebXR extensions.
Create a new Unity Project (2019.4.7f1 and up in the 2019.4.x cycle). Switch platform to WebGL.
Import WebXR Export and WebXR Interactions packages from OpenUPM.
Once packages are imported, Go to Window > WebXR > Copy WebGLTemplates.

After WebGLTemplates are in the Assets folder, Open the XR Plug-in Management tab in the Project Settings window and select the WebXR Export plug-in provider.

Now you can import the Sample Scene from Window > Package Manager > WebXR Interactions > Import into Project.

In Project Settings > Player > Resolution and Presentation, select WebXR as the WebGL Template.

Now you can build the project.
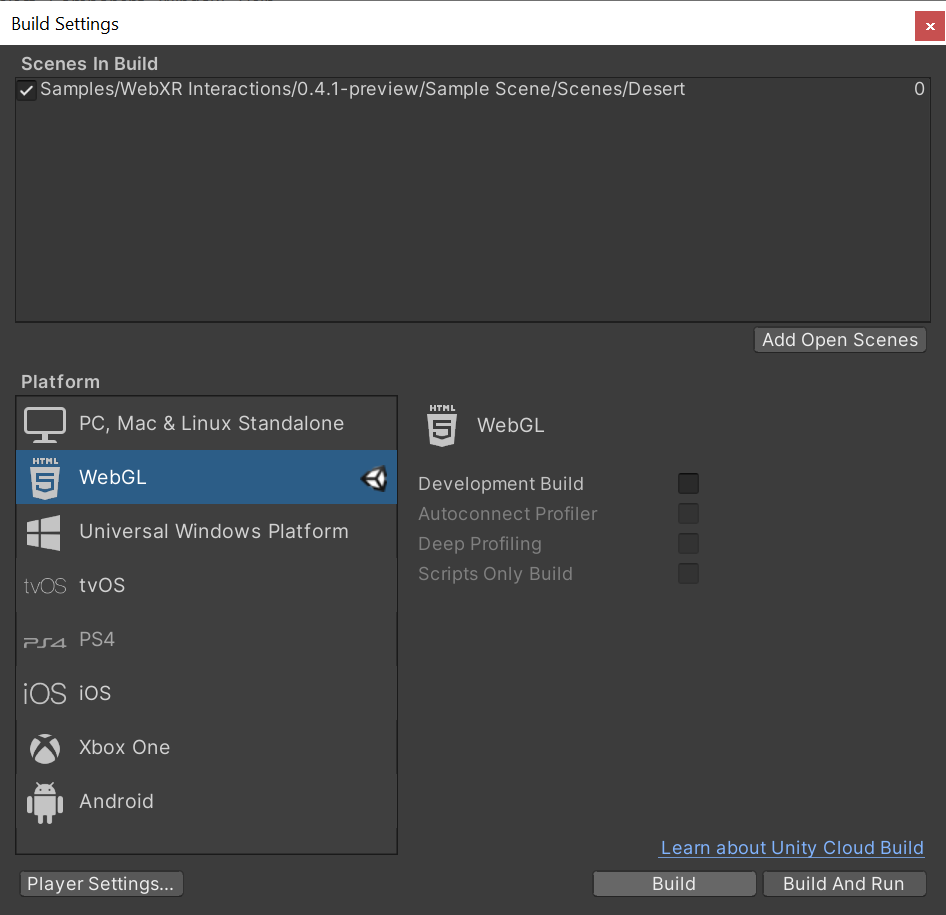
Make sure to build it from Build Settings > Build. Unity’s Build And Run server use HTTP. Run the build on your own HTTPS server.

That’s it.
Verge3D is an artist-friendly toolkit that allows Blender, 3ds Max, or Maya artists to create immersive web-based experiences. Verge3D can be used to build interactive animations, product configurators, engaging presentations of any kind, online stores, explainers, e-learning content, portfolios, and browser games.
Setting up Virtual Reality
We recommend to enable the Legacy VR option in app creation settings in the App Manager in order to support a wider range of browsers (such as Mozilla Firefox) and devices.

Cardboard devices should work out of the box in any mobile browser, both on Android and iOS.
Google Daydream works in stable Chrome browser on Android phones while HTC and Oculus devices should work in both Chrome and Firefox browsers.
Plese note that WebXR requires a secure context. Verge3D apps must be served over HTTPS/SSL, or from the localhost URL.
The VR mode can be set up for any Verge3D app using enter VR mode puzzle.

Interaction with 3D objects is performed by using the gaze-based reticle pointer automatically provided for VR devices without controllers (such as cardboards).
For VR devices with controllers, interaction is performed by the virtual ray casted from the controllers.

You can use the standard when hovered or when clicked puzzles to capture user events as well as VR-specific on session event.
Setting up Augmented Reality
You can run your Verge3D-based augmented reality applications on mobile devices with Anroid or iOS/iPadOS operating systems.
Android
To enable augmented reality, you need an Android device which supports ARCore technology and latest Google Chrome browser. You also need to install Google Play Services for AR. The installation of this package is prompted automatically upon entering AR mode for the first time, if not pre-installed.

iOS/iPadOS
Mozilla’s WebXR Viewer is a Firefox-based browser application which supports the AR technology on Apple devices (starting from iPhone 6s). Simply install it from the App Store.
Creating AR Apps
The AR mode can be set up for any Verge3D app using the enter AR mode puzzle.

Upon entering AR mode you will be able to position your 3D content in the “real” coordinate system, which is aligned with your mobile device. In addition to that, you can detect horizontal surfaces (tables, shelves, floor etc) by using the detect horizontal surface AR puzzle.
Also, to see the the real environment through your 3D canvas, you should enable the transparent background option in the configure application puzzle.

What’s Next
Check out the User Manual for more info on creating AR/VR applications with Verge3D or see the tutorials for beginners on YouTube.
Got Questions?
Feel free to ask on the forums!
Wonderland Engine is a highly performant WebXR focused development platform.
The Wonderland Editor (Windows, MacOS, Linux) makes WebXR development accessible and provides a very efficient workflow, e.g. by reloading the browser for you whenever your files change.
WebAssembly and optimizations like automatically batching your scene allow you to draw many objects without having to worry about performance.
Start with the Quick Start Guide and find a list of examples to help you get started. To start writing custom code, check out the JavaScript Getting Started Guide and refer to the JavaScript API Documentation.

Click on a tab to begin.
Tooling
Meta
The Immersive Web Emulator browser extension lets you test your WebXR enabled pages on emulated Meta Quest devices. It's very useful for approximating how your experience works in a real device and to quickly test from within your browser.WebXR Input Profiles
W3C Immersive Web Working Group
This repo provides a javascript library for managing known motion controller profiles, loading the most ideal known profile for a supplied input source, and creating a MotionController object that binds them together. Developers can use this library to interact with the conceptual components of an input source, rather than each individual button or axis.
Support Table for the WebXR Device API
If you notice missing data you can make changes on GitHub
| Feature Name | Standardisation | Polyfill | Chrome | WebXR Viewer | Magic Leap Helio | Samsung Internet | Meta Quest Browser | Microsoft Edge | Wolvic | Pico Browser | Immersive Web Emulator [Chrome] [Edge] |
| WebXR Core |
Explainer Spec MDN |
Supported, will make use of WebVR if available and WebXR is not. | Chrome 79 | iOS | Magic Leap Helio 0.98 | Samsung Internet 12.0 | 7.0, December 2019 | Edge 87 on Windows Desktop Edge 91 on Hololens 2 |
0.9.3, February 2022 | Supported | |
| WebXR AR Module |
Explainer Spec MDN |
Chrome for Android, 81 | iOS | Magic Leap Helio 0.98 | Samsung Internet 12.1 | 24.0, October 2022 | Edge 91. Hololens 2 only | ||||
| WebXR Gamepads Module |
Explainer Spec MDN |
Supported | Chrome 79 | Partially supported on Magic Leap Helio 0.98 | Samsung Internet 12.0 | 7.1, December 2019 | Edge 87 on Windows Desktop Edge 91 on Hololens 2 |
0.9.3, February 2022 | Supported | ||
| Hit Test |
Explainer Spec MDN |
Chrome for Android, 81 | IOS | Samsung Internet 12.1 | Edge 93. Hololens 2 only | ||||||
| DOM Overlays |
Explainer Spec MDN |
Chrome for Android, 83 | IOS | Samsung Internet 14.2 | |||||||
| Hand input |
Explainer Spec MDN |
15.1, April 2021 |
Edge 93. Hololens 2 only | ||||||||
| Anchors |
Explainer Spec MDN |
Chrome for Android, 85 | 15.2 | 24.0, October 2022 | Edge 93. Hololens 2 only | ||||||
| Depth Sensing |
Explainer Spec MDN |
Chrome for Android, 90 | |||||||||
| Light Estimation |
Explainer Spec MDN |
Chrome for Android, 90 | 15.2 | ||||||||
| Additional Details | Hardware Support Details | 2.0 announcement | The new Microsoft Edge for Windows Mixed Reality | Introducing Wolvic | GitHub |
[ comments ]
